Because the injection molding is a process of transforming plastic from solid (powder or pellets) to liquid (melt) and finally to solid (product). From the pellets to the melt, and then from the melt to the product, they must go through the temperature field, flow field and density field and be affected. Under the combined action of these fields, different plastics (thermosetting or thermoplastic, crystalline or non-crystalline, reinforced or non-reinforced, etc.) have different polymer structures and rheological properties.
All the factors that affect the above “field” will definitely affect the physical and mechanical properties, size, shape, precision and appearance quality of plastic products.
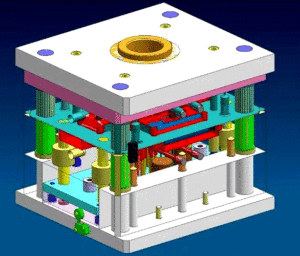
In this way, the internal connection between process factors and polymer properties, structural morphology and plastic products will be expressed through plastic products. A clear analysis of these internal connections is of great significance to rationally formulating injection molding processes, designing and manufacturing molds according to drawings, and even selecting injection molding equipment.
Precision injection molding and ordinary injection molding are also different in injection pressure and injection rate. Precision injection molding often uses high-pressure or ultra-high-pressure injection and high-speed injection to obtain a smaller molding shrinkage rate.